红外与激光工程
2023, 52(8): 20230421
1 河北工业大学先进激光技术研究中心,天津 300401
2 河北省先进激光技术与装备重点实验室,天津 300401
3 哈尔滨理工大学大珩中心-黑龙江省量子调控重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
中国激光
2022, 49(21): 2116002
强激光与粒子束
2021, 33(11): 111007
西安理工大学计算机科学与工程学院, 陕西 西安 710048
由于室内场景中存在对象种类多样、物体几何信息复杂、物体密集问题,故室内场景结构重建存在着很大的挑战。首先,以“结构分析”为主线,利用改进的随机抽样一致(RANSAC)算法和均值漂移算法检测出房间布局的粗略划分。然后,在将初步划分结果转化为无向图的基础上,利用图割算法得到了房间布局的细分结果。最后,将重建的墙壁、地面与天花板信息相结合,完成了室内场景布局的总体重建。实验结果表明,利用改进后的算法和所提方法得到的重建结果更加准确、效果更好。
图像处理 点云数据 室内场景 均值漂移算法 划分 布局重建 图割算法 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(22): 2210018
1 河北工业大学先进激光技术研究中心, 天津 300401
2 河北省先进激光技术与装备重点实验室, 天津 300401
3 麦考瑞大学物理与天文系光子研究中心, 悉尼 2109
4 国科大杭州高等研究院, 浙江 杭州 310024
中国激光
2021, 48(21): 2116003

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center for Advanced Laser Technology, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin300401, China
2 Hebei Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser Technology and Equipment, Tianjin300401, China
3 MQ Photonics Research Centre, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Macquarie University, Sydney, NSW 2109, Australia
Stimulated Raman-scattering-based lasers provide an effective way to achieve wavelength conversion. However, thermally induced beam degradation is a notorious obstacle to power scaling and it also limits the applicable range where high output beam quality is needed. Considerable research efforts have been devoted to developing Raman materials, with diamond being a promising candidate to acquire wavelength-versatile, high-power, and high-quality output beam owing to its excellent thermal properties, high Raman gain coefficient, and wide transmission range. The diamond Raman resonator is usually designed as an external-cavity pumped structure, which can easily eliminate the negative thermal effects of intracavity laser crystals. Diamond Raman converters also provide an approach to improve the beam quality owing to the Raman cleanup effect. This review outlines the research status of diamond Raman lasers, including beam quality optimization, Raman conversion, thermal effects, and prospects for future development directions.
beam quality diamond Raman conversion Raman laser thermal effects High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2021, 9(3): 03000e35
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Lasers, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
We report the measurements of Brillouin gain coefficients in FC-770, FC-40, FC-43, and FC-70 using a Brillouin oscillator and amplifier system. In contrast to the traditional way, the novel method provides direct measurements of these coefficients with the medium electro-strictive coefficient or with the phonon lifetime absent. Additionally, the Brillouin gain coefficient of FC-70 in this experiment is different from the theoretical work.
190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials 290.5900 Scattering, stimulated Brillouin 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(4): 041902
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
We obtain the output of a 284 ps pulse duration without tail modulation based on stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) pulse compression pumped by an 8 ns-pulse-duration, 1064 nm-wavelength Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. To suppress the tail modulation in SBS pulse compression, proper attenuators, which can control the pump energy within a rational range, are added in a generator-amplifier setup. The experimental result shows that the effective energy conversion efficiency triples when the pump energy reaches 700 mJ to 51%, compared with the conventional generator-amplifier setup.
190.0190 Nonlinear optics 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(9): 091901
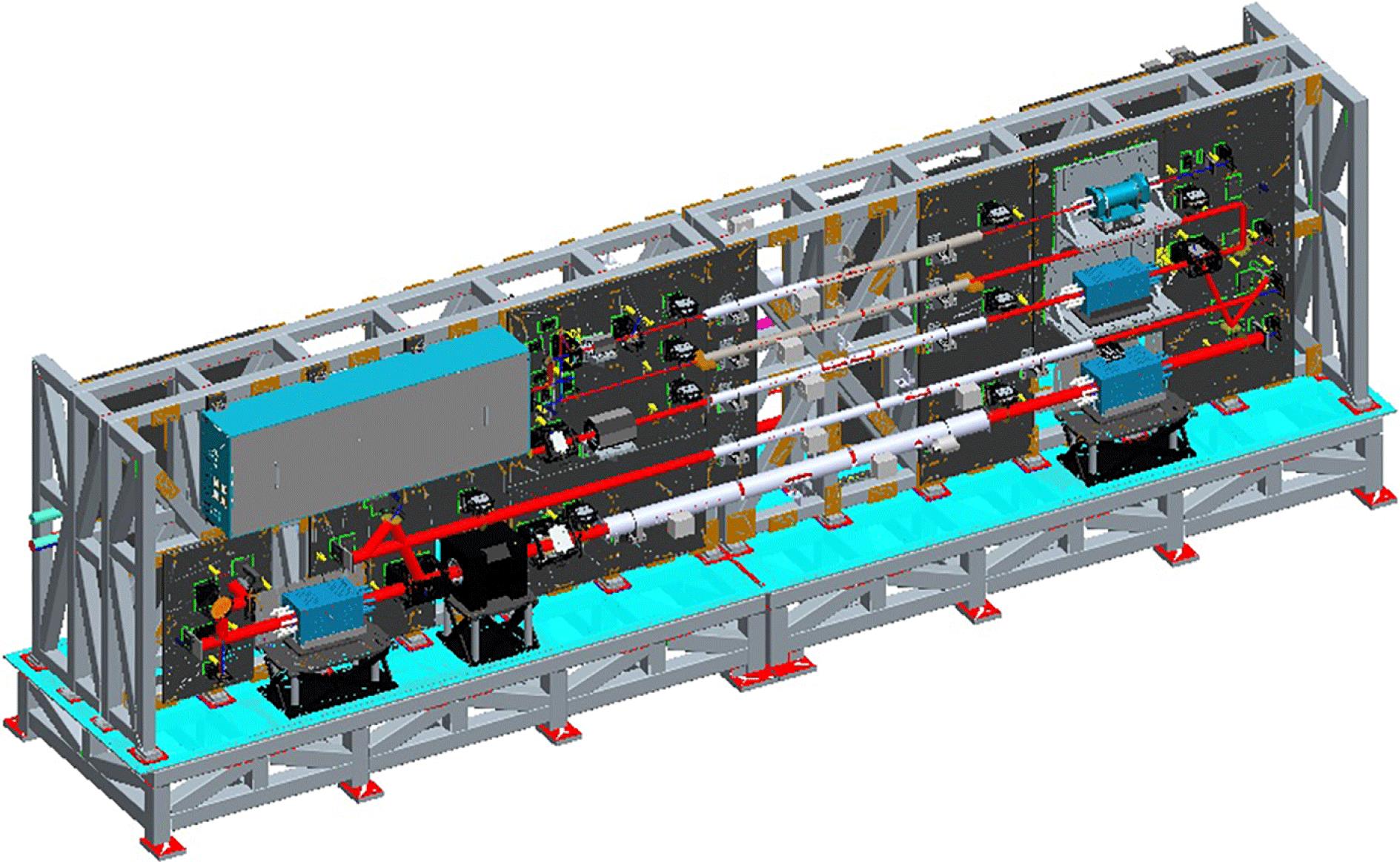
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
A 100-J-level Nd:glass laser system in nanosecond-scale pulse width has been constructed to perform as a standard source of high-fluence-laser science experiments. The laser system, operating with typical pulse durations of 3–5 ns and beam diameter 60 mm, employs a sequence of successive rod amplifiers to achieve 100-J-level energy at 1053 nm at 3 ns. The frequency conversion can provide energy of 50-J level at 351 nm. In addition to the high stability of the energy output, the most valuable of the laser system is the high spatiotemporal beam quality of the output, which contains the uniform square pulse waveform, the uniform flat-top spatial fluence distribution and the uniform flat-top wavefront.
design design frequency conversion frequency conversion laser amplifiers laser amplifiers laser engineering laser engineering laser systems laser systems light propagation light propagation modeling modeling nonlinear optics nonlinear optics optimization optimization wavefront correction wavefront correction High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2016, 4(1): 01000e10
1 中国石油天然气股份有限公司新疆油田分公司采油工艺研究院, 新疆 克拉玛依 834000
2 清华大学精密测试技术与仪器国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
提出了一种对稠油热采井下光纤非本征法布里珀罗干涉型(EFPI)永久压力传感器采集的压力信号进行小波多分辨率降噪的方法,可有效抑制传感器采集压力信号中的非平稳噪声。提出了一种基于信噪比(SNR)提升的小波分解层数确定方法,无需真实压力信号频率范围的先验知识,可通过扫描信噪比提升随小波分解层数的变化估计最优小波分解层数。在新疆某油田稠油热采井的现场试验结果表明,该方法可提高压力信号信噪比约2.6 dB,且降噪后压力信号可显著提高对油田稠油热采井原油日产量的预测准确度。
光纤光学 光纤传感器 小波分析 井下压力传感器 激光与光电子学进展
2012, 49(9): 090601





